02-08-2024, 01:43 AM
Thanks. I (rarely) use QGIS, a bit much for the casual mapping, but since it is free fine. While I like to add some genetic info, building own maps from the supporting sciences like climatology would be a bit much for an outsider and I would like to rely on good sources. I will try to search the linked database.
This population density maps trough the last Ice Age are informative, but i is difficult to evaluate how much confidence can be put in the reconstruction. Unfortunate that West/Central Asia is not included as the Siberia and Middle East situation would certainly allow to see the overall refugiums impacting main pop expansions and Europe later better.
This population density maps trough the last Ice Age are informative, but i is difficult to evaluate how much confidence can be put in the reconstruction. Unfortunate that West/Central Asia is not included as the Siberia and Middle East situation would certainly allow to see the overall refugiums impacting main pop expansions and Europe later better.
Quote:Human population dynamics in Europe over the Last Glacial Maximum
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1503784112
Abstract
The severe cooling and the expansion of the ice sheets during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), 27,000–19,000 y ago (27–19 ky ago) had a major impact on plant and animal populations, including humans. Changes in human population size and range have affected our genetic evolution, and recent modeling efforts have reaffirmed the importance of population dynamics in cultural and linguistic evolution, as well. However, in the absence of historical records, estimating past population levels has remained difficult. Here we show that it is possible to model spatially explicit human population dynamics from the pre-LGM at 30 ky ago through the LGM to the Late Glacial in Europe by using climate envelope modeling tools and modern ethnographic datasets to construct a population calibration model. The simulated range and size of the human population correspond significantly with spatiotemporal patterns in the archaeological data, suggesting that climate was a major driver of population dynamics 30–13 ky ago. The simulated population size declined from about 330,000 people at 30 ky ago to a minimum of 130,000 people at 23 ky ago. The Late Glacial population growth was fastest during Greenland interstadial 1, and by 13 ky ago, there were almost 410,000 people in Europe. Even during the coldest part of the LGM, the climatically suitable area for human habitation remained unfragmented and covered 36% of Europe.
Simulated human population range and density compared with the spatial distribution of archaeological sites during six time intervals from 30 to 13 ky ago. Archaeological sites are indicated with black dots and in each time slice they represent sites dated within 1,000-y bins.

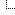


![[Image: pnas.1503784112fig02.jpeg]](https://www.pnas.org/cms/10.1073/pnas.1503784112/asset/b0555c41-4efa-4e7e-8ff7-481882ff87ed/assets/graphic/pnas.1503784112fig02.jpeg)